OCT analysis
OCT is the abbreviation for Optical Coherence Tomography (or OCT).

OCT (OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY)
With this technique, sectional images of the anterior eye segments or the fundus of the eye can be taken in high resolution (3 to 5 μm). OCT works similar to an ultrasound examination, but instead of sound waves, laser beams are used to show tissue density in different areas based on the reflection. The use of low energy laser light enables a resolution about 20-times higher than that of conventional ultrasound.
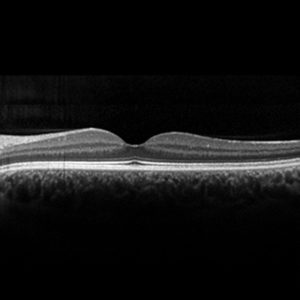
As a modern examination method, OCT is particularly helpful for various diseases of the ocular fundus. It allows, for example, an exact image of the retinal thickness. It is used in macular foramen (formation of holes in the retina), age-related macular degeneration (increase in retinal thickness due to water retention or detachment), diabetic retinopathy (retinal changes due to diabetes) or glaucoma.
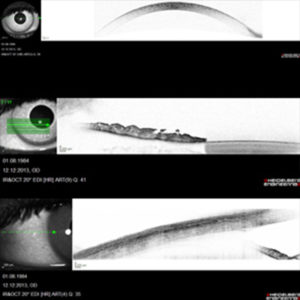
ANTERIOR SEGMENT OCT
With a special lens attachment, measurements of the cornea, sclera and iris can be achieved.
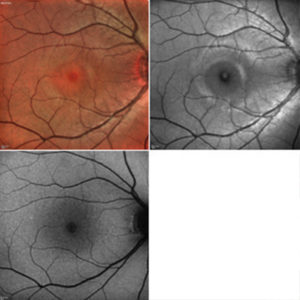
MULTICOLOR, REDFREE AND AUTOFLUORESCENCE IMAGES
With Multicolor, Redfree and Autofluorescence the different layers in the eye can be documented individually. This serves the differentiated diagnosis.

